Economy and Social Justice
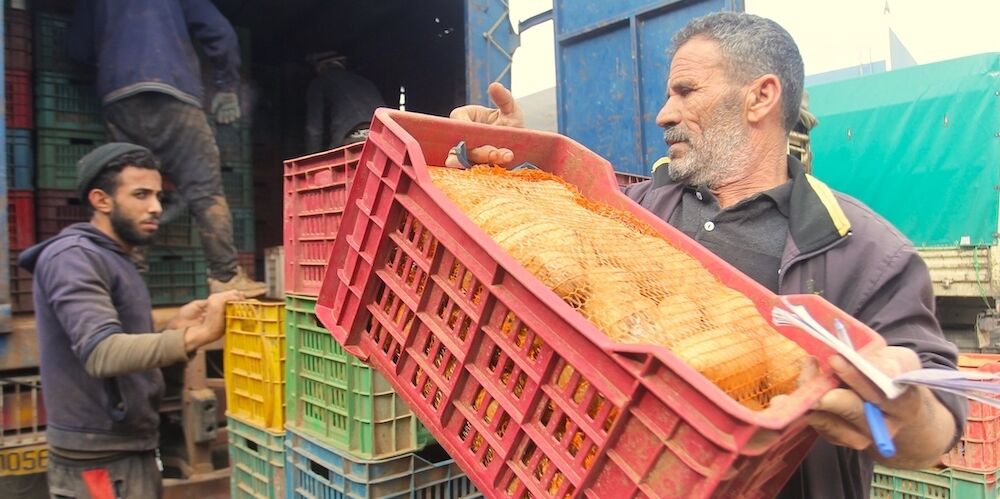

While socio-economic factors were an important driver for the protest movements in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region in 2010/11, most of the countries continue to follow a neoliberal economic model. Some governments were able to secure social peace through rentier income, but this has become less and less successful due to the decline in the oil price. Structural deficits in economic policy, such as the high dependence on the energy sector, the need for labour market policy reform, low productivity, and a low rate of industrialisation, are thus becoming increasingly apparent.
Due to economic and financial difficulties, many countries in the region have had to call on the support of international financial institutions such as the World Bank or the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Tied to this financial support were structural adjustment conditions that were supposed to increase the countries' international competitiveness. However, a side effect of liberalisation, privatisation, and the reduction of state services is growing social inequality. The economic growth achieved benefited a small and well-connected elite and entrenched clientelist structures of power.
Increasing social inequality in the region has a negative impact on the development of the respective countries, not only economically, but also socially and politically. Inadequate social security systems in need of reform, a dramatic increase in informal employment and the unfulfilled hope of social advancement through education are leading to increasing resignation and a lack of prospects, especially among young people.
With its regional project Economic Policies for Social Justice, based in Tunis, the Friedrich-Ebert-Stiftung (FES) aims to revitalise the debate on economic policy in the region. Instead of the discussion being stuck in the rut of structural adjustment and austerity measures that are believed to be "without alternative", real economic policy alternatives are to be considered. These should contribute to strengthening social justice in the economies of the region.
Publications
Parsi, Rouzbeh
Great expectations
Berlin, 2016
Download publication (175 KB, PDF-File)
Corporate social responsibility in the EU and in Israel
Herzliya, 2015
[The alliance for a social Israel
Herzliya, 2015
The future of Jordan's qualified industrial Zones
Amman, 2014
Download publication (750 KB, PDF-File)
Grammling, Steffen
Current and future challenges for the multilateral trading system
Genf;Bonn, 2008
Download publication (250 KB, PDF-File)